| Identification |
| Name: | b-D-Glucopyranose,1,6-anhydro-2,3,4-tris-O-(phenylmethyl)- |
| Synonyms: | Glucopyranose,1,6-anhydro-2,3,4-tri-O-benzyl-, b-D- (7CI,8CI);1,6-Anhydro-2,3,4-tri-O-benzyl-b-D-glucopyranose;Tri-O-benzyllevoglucosan; |
| CAS: | 10548-46-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C27H28O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 432.51 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C27H28O5/c1-4-10-20(11-5-1)16-28-24-23-19-31-27(32-23)26(30-18-22-14-8-3-9-15-22)25(24)29-17-21-12-6-2-7-13-21/h1-15,23-27H,16-19H2/t23-,24-,25+,26-,27-/m1/s1 |
| Molecular Structure: |
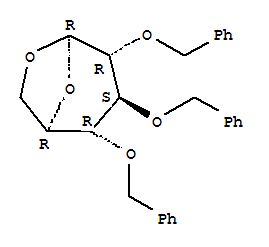 |
| Properties |
| Flash Point: | 220.8°C |
| Boiling Point: | 555.8°C at 760 mmHg |
| Density: | 1.22g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.611 |
| Specification: |
Off-White Solid
usageEng:1,6-Anhydrohexopyranoses have proven to be valuable synthons for the preparation of biologically important and structurally diverse products (e.g. rifamycin S, indanomycin, thromboxane B2, (+)-biotin, tetrodotoxin, quinone, and macrolide antibiotics) as |
| Flash Point: | 220.8°C |
| Usage: | 1,6-Anhydrohexopyranoses have proven to be valuable synthons for the preparation of biologically important and structurally diverse products (e.g. rifamycin S, indanomycin, thromboxane B2, (+)-biotin, tetrodotoxin, quinone, and macrolide antibiotics) as |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |