| Identification |
| Name: | Benzenecarboperoxoicacid, 1,1'-(1,1,4,4-tetramethyl-1,4-butanediyl) ester |
| Synonyms: | Benzenecarboperoxoicacid, 1,1,4,4-tetramethyl-1,4-butanediyl ester (9CI); Peroxybenzoic acid,1,1,4,4-tetramethyltetramethylene ester (7CI,8CI); 2,5-Hexanediol,2,5-dimethyl-, bis(peroxybenzoate) (8CI);2,5-Bis(benzoyldioxy)-2,5-dimethylhexane;2,5-Bis(benzoylperoxy)-2,5-dimethylhexane;2,5-Dibenzoylperoxy-2,5-dimethylhexane; 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-bis(benzoylperoxy)hexane;2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-di(benzoylperoxy)hexane;2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexanedihydroperoxide dibenzoate; 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexanediolbis(peroxybenzoate); 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol diperoxybenzoate;2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexanediyl bis(peroxybenzoate); 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexanediylperoxybenzoate; 2,5-Dimethylhexane-2,5-diperoxybenzoate;2,5-Dimethylhexane-2,5-diyl diperbenzoate; Kayaester AB; L 118; Luperox 118;Lupersol 118; Perhexa 25Z; USP 711 |
| CAS: | 2618-77-1 |
| EINECS: | 220-050-9 |
| Molecular Formula: | C22H26 O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 386.4382 |
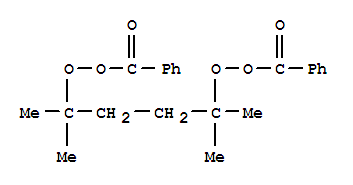
| InChI: | InChI=1/C22H26O6/c1-21(2,27-25-19(23)17-11-7-5-8-12-17)15-16-22(3,4)28-26-20(24)18-13-9-6-10-14-18/h5-14H,15-16H2,1-4H3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | 3102 |
| Density: | 1.143 g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.534 |
| Specification: |
2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-Di(Benzoylperoxy)Hexane is particularly sensitive to temperature rises and contamination. Above a given "Control Temperature" they decompose violently. It is generally stored or transported as a mixture, with an inert solid. To reactivity profile peroxides, such as 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-Di(Benzoylperoxy)Hexane , are good oxidizing agents. Organic compounds can ignite on contact with concentrated peroxides. Strongly reduced material such as sulfides, nitrides, and hydrides may react explosively with peroxides. There are few chemical classes that do not at least produce heat when mixed with peroxides. Many produce explosions or generate gases (toxic and nontoxic). Generally, dilute solutions of peroxides (<70%) are safe, but the presence of a catalyst (often a transition metal such as cobalt, iron, manganese, nickel, or vanadium) as an impurity may even then cause rapid decomposition, a buildup of heat, and even an explosion. Solutions of peroxides often become explosive when evaporated to dryness or near-dryness. Danger of explosion when dry. May explode from heat, shock, friction or contamination. May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames.
|
| Packinggroup: | II |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |