| Identification |
| Name: | 1,1'-Biphenyl,2,3,3',4,4',5-hexachloro- |
| Synonyms: | 2,3,3',4,4',5-Hexachloro-1,1'-biphenyl;2,3,3',4,4',5-Hexachlorobiphenyl; 2,3,4,4',5,5'-Hexachlorobiphenyl;2,3,4,5,3',4'-Hexachlorobiphenyl; 3,4,2',3',4',5'-Hexachlorobiphenyl; CB 156;PCB 156 |
| CAS: | 38380-08-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C12H4 Cl6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 360.86 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C12H4Cl6/c13-7-2-1-5(3-8(7)14)6-4-9(15)11(17)12(18)10(6)16/h1-4H |
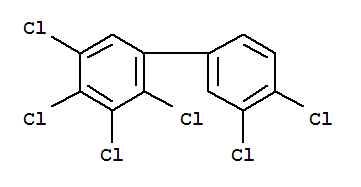
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | UN 1208 3/PG 2 |
| Density: | 1.593 g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.626 |
| Specification: |
The model chemicals, benzo[a]pyrene (BaP, 2.5 mg kg-1), 2,3,3′,4,4′,5-Hexachlorobiphenyl (CAS NO.38380-08-4)(PCB-156, 2.5 mg kg-1), and cadmium (cadmium, 1 mg kg-1), were administered to fish by subcutaneous injections. Biomarker responses were quantified both following administration of single chemicals and sequential combinations of the chemicals in pairs. Significant induction of CYP1A protein levels and corresponding ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activities was observed in BaP and PCB treated flounder after 2 and 8 days, respectively. The strongest induction (44 fold) was caused by BaP. No further induction was observed after additional treatment with PCB 156. CYP1A induction caused by BaP was inhibited (40% compared with BaP treatment alone) in flounder pre treated with cadmium, whereas induction by PCB 156 appeared to be unaffected by pre treatment with cadmium.
|
| Storage Temperature: | 2-8°C |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
|
| |
 |