| Identification |
| Name: | b-D-Glucopyranuronic acid,1-retinoate |
| Synonyms: | Retinoicacid, 1-ester with glucopyranuronic acid (7CI); Retinoic acid, 1-ester with b-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid(8CI); Glucopyranosiduronic acid, 1-retinoate, b-D- (8CI); Retinoic acid, b-D-glucopyranuronic acid deriv.; Retinoic acid, b-D-glucuronosyl ester; Retinoyl b-glucuronide; all-trans-Retinoylglucuronide; all-trans-Retinoyl b-D-glucuronide |
| CAS: | 401-10-5 |
| Molecular Formula: | C26H36 O8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 0 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C26H36O8/c1-15(11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-26(18,4)5)8-6-9-16(2)14-19(27)33-25-22(30)20(28)21(29)23(34-25)24(31)32/h6,8-9,11-12,14,20-23,25,28-30H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,31,32)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8+,16-14+/t20-,21-,22+,23-,25+/m0/s1 |
| Molecular Structure: |
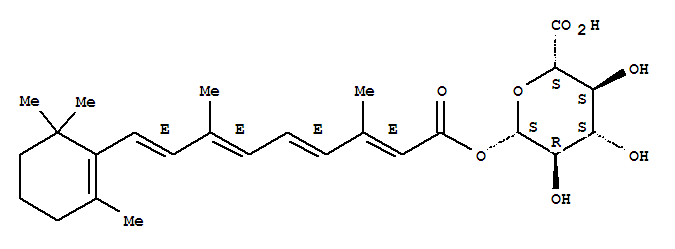 |
| Properties |
| Flash Point: | 220.1°C |
| Boiling Point: | 670.4°Cat760mmHg |
| Density: | 1.24g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.578 |
| Specification: |
Yellow Solid
usageEng:A biliary metabolite of Vitamin A, occurs endogenously in human blood. RAG is biologically active in promoting the growth of vitamin A-deficient rats and the the induction of differentiation of HL-60 and BA-HAN-1C cells, but less cytotoxic than Retinoic Acids. |
| Flash Point: | 220.1°C |
| Usage: | A biliary metabolite of Vitamin A, occurs endogenously in human blood. RAG is biologically active in promoting the growth of vitamin A-deficient rats and the the induction of differentiation of HL-60 and BA-HAN-1C cells, but less cytotoxic than Retinoic Acids. |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |