| Identification |
| Name: | Benzamide, N-hydroxy- |
| Synonyms: | Benzohydroxamicacid (6CI,8CI); BHAM; Benzenehydroxamic acid; Benzhydroxamic acid;Benzohydroximic acid; Benzoylhydroxylamine; Hydroxylamine, N-benzoyl-;N-Benzohydroxamic acid; N-Benzoylhydroxylamine; N-Hydroxybenzamide; NSC 147248;NSC 3136; Phenylhydroxamic acid |
| CAS: | 495-18-1 |
| EINECS: | 207-797-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C7H7 N O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 137.14 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C7H7NO2/c9-7(8-10)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5,10H,(H,8,9) |
| Molecular Structure: |
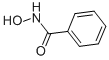 |
| Properties |
| Density: | 1.237 g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. |
| Solubility: | 22 g/L (6 ºC) |
| Appearance: | brownish crystalline powder |
| Specification: |
1.Reactivity Profile :Benzohydroxamic acid is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
2.Health Hazard :acute/chronic hazards : When heated to decomposition Benzohydroxamic acid emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
3.Fire Hazard :Flash point data for Benzohydroxamic acid are not available; however, Benzohydroxamic acid is probably combustible.
|
| Report: |
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory. EPA Genetic Toxicology Program.
|
| HS Code: | 29280090 |
| Storage Temperature: | 0-6°C |
| Usage: | Fungicide. |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
 Xn:Harmful
Xn:Harmful
|
| |
 |