| Identification |
| Name: | Furosemide |
| Synonyms: | 5-(aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-2-((2-furanylmethyl)amino)benzoic acid; 4-chloro-n-furfuryl-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid; 2-furfurylamino-4-chloro-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid |
| CAS: | 54-31-9 |
| EINECS: | 200-203-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C12H11ClN2O5S |
| Molecular Weight: | 330.74414 |
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C12H11ClN2O5S/c13-9-5-10(15-6-7-2-1-3-20-7)8(12(16)17)4-11(9)21(14,18)19/h1-5,15H,6H2,(H,16,17)(H2,14,18,19) |
| Molecular Structure: |
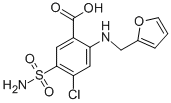 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | UN 1230 3/PG 2 |
| Density: | 1.606 |
| Stability: | Stable, but light sensitive, air sensitive and hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility: | Slightly soluble in water |
| Solubility: | Slightly soluble in water |
| Appearance: | white powder |
| Specification: |
Furosemide may undergo hydrolysis at sufficiently low pH. The pH of aqueous solutions should be maintained in the basic range to prevent hydrolysis. Alcohol has been shown to improve the stability of Furosemide. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents .
|
| Biological Activity: | Loop diuretic that inhibits the Na + /2Cl - /K + (NKCC) cotransporter. Also acts as a non-competitive antagonist at GABA A receptors with ~ 100-fold greater selectivity for α 6-containing receptors than α 1-containing receptors. |
| Storage Temperature: | 2-8°C |
| Color: | Crystals from aqueous ethanol
Yellow powder
FINE, WHITE TO SLIGHTLY YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER |
| Usage: | Used as a diuretic |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
 T:Toxic
T:Toxic
|
| |
 |