| Identification |
| Name: | Diphenylthiocarbazone |
| Synonyms: | Dithizone |
| CAS: | 60-10-6 |
| EINECS: | 200-454-1 |
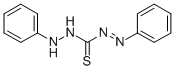
| Molecular Formula: | C13H12N4S |
| Molecular Weight: | 256.32618 |
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C13H12N4S/c18-13(16-14-11-7-3-1-4-8-11)17-15-12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10,14H,(H,16,18) |
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | OTH |
| Flash Point: | 167.208°C |
| Boiling Point: | 352.866°C at 760 mmHg |
| Density: | 1.217g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Refractive index: | 1.648 |
| Water Solubility: | Insoluble |
| Solubility: | Insoluble |
| Appearance: | dark blue solid |
| Specification: |
Diphenylthiocarbazone (60-10-6) is a sulfur-containing organic compound. It is a good ligand, and forms complexes with many metals such as lead and mercury.It may be prepared by reacting phenylhydrazine with carbon disulfide, followed by reaction with potassium hydroxide.
|
| Report: |
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
|
| Packinggroup: | III |
| Flash Point: | 167.208°C |
| Usage: | Dithizone is an organosulfur compound that acts as a chelating agent and forms complexes with metals such as lead and mercury. Dithizone is used to assess the purity of human pancreatic islet preparations used for transplantation into patients with type 1 diabetes. |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
 Xi:Irritant
Xi:Irritant
|
| |
 |