| Identification |
| Name: | Hexanamide |
| Synonyms: | Caproamide;Caproic amide;Capromide;Capronamide;Hexylamide;NSC 8437;n-Caproamide;n-Hexanamide; |
| CAS: | 628-02-4 |
| EINECS: | 211-024-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C6H13NO |
| Molecular Weight: | 115.17352 |
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C6H13NO/c1-2-3-4-5-6(7)8/h2-5H2,1H3,(H2,7,8) |
| Molecular Structure: |
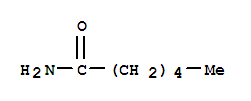 |
| Properties |
| Boiling Point: | 255 C |
| Density: | 0.897 g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with acids, bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility: | slight Stability Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with acids, bases, strongoxidizing agents. Toxicology Skin, eye and respiratory irritant. Toxicity data (The m |
| Solubility: | slight |
| Appearance: | colourless crystalline solid |
| Specification: |
Reactivity Profile:Hexanamide is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx). Can react with mineral acids and bases.
|
| Report: |
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
|
| Color: | CRYSTALS FROM ACETONE |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |