| Identification |
| Name: | 1H-Purine-2,6-dione,3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-tri(methyl-d3)- |
| Synonyms: | CAFFEINE-D9 (1,3,7-TRIMETHYL-D9);Caffeine (1,3,7-Trimethyl-D9);3,7-Dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-d9-1H-purine-2,6-dione;Caffeine-d9;Coffeine-d;Oxopurine-d9;Coffeine-d9 |
| CAS: | 72238-85-8 |
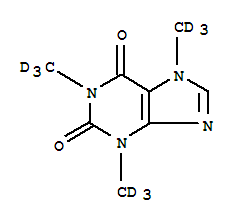
| Molecular Formula: | C8H D9 N4 O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 203.25 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C8H10N4O2/c1-10-4-9-6-5(10)7(13)12(3)8(14)11(6)2/h4H,1-3H3/i1D3,2D3,3D3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Melting Point: | 2380C |
| Flash Point: | 205.867°C |
| Boiling Point: | 416.789°C at 760 mmHg |
| Density: | 1.524g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.679 |
| Specification: |
Crystalline Solid
usageEng:Lablled Caffeine (C080100). Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline xanthine alkaloid that acts as a stimulant drug and a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the seeds, leaves, and fruit of some plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants.
In humans, caffeine acts as a central nervous system stimulant, temporarily warding off drowsiness and restoring alertness. Caffeine is a cardiac and respiratory stimulant; diuretic. Caffeine is toxic at sufficiently high doses. |
| Flash Point: | 205.867°C |
| Usage: | Cardiac and respiratory stimulant; diuretic |
| Safety Data |
| |
 |