| Identification |
| Name: | Calcium |
| Synonyms: | CalciumshotNmmdia; CalciumturningsN; Calciumshavings; CalciumcrystallinedendriticsolidNampouledunderargon; Calciumgranulesmesh; Calcium shot; Calcium turnings; Calcium solution 1000 ppm; Calcium solution 10 000 ppm |
| CAS: | 7440-70-2 |
| EINECS: | 231-179-5 |
| Molecular Formula: | Ca |
| Molecular Weight: | 40.08 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/Ca |
| Molecular Structure: |
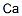 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | UN 1401 4.3/PG 2 |
| Density: | 1.54 |
| Stability: | Stable, but reacts with water to release hydrogen and produce calcium hydroxide. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alcohols, moisture. |
| Water Solubility: | Decomposes in water, alcohol and acids to H2 |
| Solubility: | Decomposes in water, alcohol and acids to H2 |
| Appearance: | softish silver-white metal |
| Specification: |
? Calcium (CAS NO.7440-70-2), its Synonyms are Elemental calcium ; HSDB 273 ; UNII-SY7Q814VUP . It is silvery, soft metal that turns grayish white on exposure to air. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth most abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust. Calcium is also the fifth most abundant dissolved ion in seawater by both molarity and mass, after sodium, chloride, magnesium, and sulfate.
|
| Packinggroup: | II |
| Storage Temperature: | water-free area |
| Color: | Lustrous, silver-white surface (when freshly cut); face-centered cubic structure below 300 deg C; acquires bluish-gray tarnish on exposure to moist air
Silvery-white metal |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
 F:Highlyflammable
F:Highlyflammable
|
| |
 |