| Identification |
| Name: | Benzenesulfonamide, N-ethyl-2(or 4)-methyl- |
| Synonyms: | AI3-04487;AI3-08014;CCRIS 6102;Ketjenflex 8;N-Ethyl-2(or 4)-methylbenzenesulfonamide;N-Ethyl-o(or p)-tol uenesulfonamide;Santicizer 8;Toluene ethylsulfonamide;N-Ethyl-o(or p)-toluenesulphonamide;N-Ethyltoluenesulfonamide; |
| CAS: | 8047-99-2 |
| EINECS: | 232-465-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C9H13NO2S |
| Molecular Weight: | 199.29 |
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C9H13NO2S/c1-3-10-13(11,12)9-6-4-8(2)5-7-9/h4-7,10H,3H2,1-2H3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
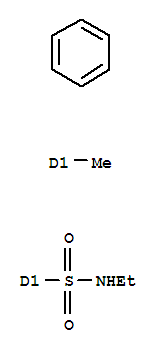 |
| Properties |
| Density: | 1.153 g/cm3 |
| Water Solubility: | | <0.01 G/100 ML AT 18 ºC |
| Specification: |
Benzenesulfonamide, N-ethyl-2(or 4)-methyl- (CAS NO.8047-99-2) is a viscous slightly yellow liquid. It is insoluble in water. Also it is an amide. Amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).And it is probably combustible.
|
| Safety Data |
| |
 |