| Identification |
| Name: | Carbamic acid,N,N-dimethyl-, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl ester |
| Synonyms: | Carbamicacid, dimethyl-, 3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl ester (9CI); Carbamic acid,dimethyl-, 3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-yl ester (6CI,7CI,8CI);3-Methyl-1-phenylpyrazol-5-yl dimethylcarbamate; G 22008; NSC 404297; Pyrolan |
| CAS: | 87-47-8 |
| EINECS: | 211-694-1 |
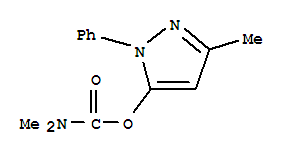
| Molecular Formula: | C13H15 N3 O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 245.31 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C13H15N3O2/c1-10-9-12(18-13(17)15(2)3)16(14-10)11-7-5-4-6-8-11/h4-9H,1-3H3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | 2757 |
| Melting Point: | 50 C |
| Flash Point: | 178.7°C |
| Boiling Point: | 160 - 162 C at 0.2 mm Hg |
| Density: | 1.15g/cm3 |
| Stability: | Stability Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Refractive index: | 1.573 |
| Water Solubility: | soluble |
| Solubility: | soluble |
| Appearance: | crystalline solid |
| Specification: |
1.Reactivity Profile: Pyrolan (CAS NO. 87-47-8) is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
2.Health Hazard: Acute/chronic hazards: Pyrolan. is a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
3.Fire Hazard :Flash point data for Pyrolan. are not available; however, Pyrolan. is probably combustible.
|
| Packinggroup: | III |
| Flash Point: | 178.7°C |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
|
| |
 |