| Identification |
| Name: | 2-Pentanol, 4-methyl-,2-acetate |
| Synonyms: | 2-Pentanol,4-methyl-, acetate (6CI,7CI,8CI,9CI); 1,3-Dimethylbutyl acetate;4-Methyl-2-pentanol acetate; 4-Methyl-2-pentyl acetate; 4-Methylpent-2-ylethanoate; Acetic acid 1,3-dimethylbutyl ester; MAAc; Methylisobutylcarbinolacetate; NSC 567 |
| CAS: | 108-84-9 |
| EINECS: | 203-621-7 |
| Molecular Formula: | C8H16 O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 144.24 |
| InChI: | InChI=1/C8H16O2/c1-4-5-6-7(2)10-8(3)9/h7H,4-6H2,1-3H3 |
| Molecular Structure: |
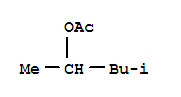 |
| Properties |
| Transport: | 3272 |
| Melting Point: | -63.8 |
| Density: | 0,86 g/cm3 |
| Refractive index: | 1.411 |
| Solubility: | Very soluble in ethyl ether and ethanol.
0.08 G/100 ML WATER
0.13%WT in aq, 20 deg C; 0.57%w aq in, 20 deg C
Miscible with alcohol |
| Appearance: | COLOURLESS LIQUID , WITH CHARACTERISTIC ODOUR |
| Specification: |
It is incompatible with the following: Nitrates; strong oxidizers, alkalis & acids .It is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides.
|
| Report: |
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
|
| Packinggroup: | III |
| Color: | Colorless liquid. |
| Safety Data |
| Hazard Symbols |
 Moderate fire risk. Toxic by inhalation. TLV: 50
Moderate fire risk. Toxic by inhalation. TLV: 50
|
| |
 |